Java 推箱子
原文: https://zetcode.com/tutorials/javagamestutorial/sokoban/
在 Java 2D 游戏教程的这一部分中,我们将创建 Java 推箱子游戏克隆。 源代码和图像可以在作者的 Github Java-Sokoban-Game 存储库中找到。
推箱子
推箱子是另一个经典的电脑游戏。 它由 Imabayashi Hiroyuki 于 1980 年创建。 推箱子是日语的仓库管理员。 玩家在迷宫周围推箱子。 目的是将所有盒子放置在指定的位置。
Java 推箱子游戏的开发
我们使用光标键控制推箱子对象。 我们也可以按 R 键重新启动电平。 将所有行李放在目的地区域后,游戏结束。 我们在窗口的左上角绘制"Completed"字符串。
Board.java
package com.zetcode;
import java.awt.Color;
import java.awt.Graphics;
import java.awt.event.KeyAdapter;
import java.awt.event.KeyEvent;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
public class Board extends JPanel {
private final int OFFSET = 30;
private final int SPACE = 20;
private final int LEFT_COLLISION = 1;
private final int RIGHT_COLLISION = 2;
private final int TOP_COLLISION = 3;
private final int BOTTOM_COLLISION = 4;
private ArrayList<Wall> walls;
private ArrayList<Baggage> baggs;
private ArrayList<Area> areas;
private Player soko;
private int w = 0;
private int h = 0;
private boolean isCompleted = false;
private String level
= " ######\n"
+ " ## #\n"
+ " ##$ #\n"
+ " #### $##\n"
+ " ## $ $ #\n"
+ "#### # ## # ######\n"
+ "## # ## ##### ..#\n"
+ "## $ $ ..#\n"
+ "###### ### #@## ..#\n"
+ " ## #########\n"
+ " ########\n";
public Board() {
initBoard();
}
private void initBoard() {
addKeyListener(new TAdapter());
setFocusable(true);
initWorld();
}
public int getBoardWidth() {
return this.w;
}
public int getBoardHeight() {
return this.h;
}
private void initWorld() {
walls = new ArrayList<>();
baggs = new ArrayList<>();
areas = new ArrayList<>();
int x = OFFSET;
int y = OFFSET;
Wall wall;
Baggage b;
Area a;
for (int i = 0; i < level.length(); i++) {
char item = level.charAt(i);
switch (item) {
case '\n':
y += SPACE;
if (this.w < x) {
this.w = x;
}
x = OFFSET;
break;
case '#':
wall = new Wall(x, y);
walls.add(wall);
x += SPACE;
break;
case '$':
b = new Baggage(x, y);
baggs.add(b);
x += SPACE;
break;
case '.':
a = new Area(x, y);
areas.add(a);
x += SPACE;
break;
case '@':
soko = new Player(x, y);
x += SPACE;
break;
case ' ':
x += SPACE;
break;
default:
break;
}
h = y;
}
}
private void buildWorld(Graphics g) {
g.setColor(new Color(250, 240, 170));
g.fillRect(0, 0, this.getWidth(), this.getHeight());
ArrayList<Actor> world = new ArrayList<>();
world.addAll(walls);
world.addAll(areas);
world.addAll(baggs);
world.add(soko);
for (int i = 0; i < world.size(); i++) {
Actor item = world.get(i);
if (item instanceof Player || item instanceof Baggage) {
g.drawImage(item.getImage(), item.x() + 2, item.y() + 2, this);
} else {
g.drawImage(item.getImage(), item.x(), item.y(), this);
}
if (isCompleted) {
g.setColor(new Color(0, 0, 0));
g.drawString("Completed", 25, 20);
}
}
}
@Override
public void paintComponent(Graphics g) {
super.paintComponent(g);
buildWorld(g);
}
private class TAdapter extends KeyAdapter {
@Override
public void keyPressed(KeyEvent e) {
if (isCompleted) {
return;
}
int key = e.getKeyCode();
switch (key) {
case KeyEvent.VK_LEFT:
if (checkWallCollision(soko,
LEFT_COLLISION)) {
return;
}
if (checkBagCollision(LEFT_COLLISION)) {
return;
}
soko.move(-SPACE, 0);
break;
case KeyEvent.VK_RIGHT:
if (checkWallCollision(soko, RIGHT_COLLISION)) {
return;
}
if (checkBagCollision(RIGHT_COLLISION)) {
return;
}
soko.move(SPACE, 0);
break;
case KeyEvent.VK_UP:
if (checkWallCollision(soko, TOP_COLLISION)) {
return;
}
if (checkBagCollision(TOP_COLLISION)) {
return;
}
soko.move(0, -SPACE);
break;
case KeyEvent.VK_DOWN:
if (checkWallCollision(soko, BOTTOM_COLLISION)) {
return;
}
if (checkBagCollision(BOTTOM_COLLISION)) {
return;
}
soko.move(0, SPACE);
break;
case KeyEvent.VK_R:
restartLevel();
break;
default:
break;
}
repaint();
}
}
private boolean checkWallCollision(Actor actor, int type) {
switch (type) {
case LEFT_COLLISION:
for (int i = 0; i < walls.size(); i++) {
Wall wall = walls.get(i);
if (actor.isLeftCollision(wall)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
case RIGHT_COLLISION:
for (int i = 0; i < walls.size(); i++) {
Wall wall = walls.get(i);
if (actor.isRightCollision(wall)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
case TOP_COLLISION:
for (int i = 0; i < walls.size(); i++) {
Wall wall = walls.get(i);
if (actor.isTopCollision(wall)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
case BOTTOM_COLLISION:
for (int i = 0; i < walls.size(); i++) {
Wall wall = walls.get(i);
if (actor.isBottomCollision(wall)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
default:
break;
}
return false;
}
private boolean checkBagCollision(int type) {
switch (type) {
case LEFT_COLLISION:
for (int i = 0; i < baggs.size(); i++) {
Baggage bag = baggs.get(i);
if (soko.isLeftCollision(bag)) {
for (int j = 0; j < baggs.size(); j++) {
Baggage item = baggs.get(j);
if (!bag.equals(item)) {
if (bag.isLeftCollision(item)) {
return true;
}
}
if (checkWallCollision(bag, LEFT_COLLISION)) {
return true;
}
}
bag.move(-SPACE, 0);
isCompleted();
}
}
return false;
case RIGHT_COLLISION:
for (int i = 0; i < baggs.size(); i++) {
Baggage bag = baggs.get(i);
if (soko.isRightCollision(bag)) {
for (int j = 0; j < baggs.size(); j++) {
Baggage item = baggs.get(j);
if (!bag.equals(item)) {
if (bag.isRightCollision(item)) {
return true;
}
}
if (checkWallCollision(bag, RIGHT_COLLISION)) {
return true;
}
}
bag.move(SPACE, 0);
isCompleted();
}
}
return false;
case TOP_COLLISION:
for (int i = 0; i < baggs.size(); i++) {
Baggage bag = baggs.get(i);
if (soko.isTopCollision(bag)) {
for (int j = 0; j < baggs.size(); j++) {
Baggage item = baggs.get(j);
if (!bag.equals(item)) {
if (bag.isTopCollision(item)) {
return true;
}
}
if (checkWallCollision(bag, TOP_COLLISION)) {
return true;
}
}
bag.move(0, -SPACE);
isCompleted();
}
}
return false;
case BOTTOM_COLLISION:
for (int i = 0; i < baggs.size(); i++) {
Baggage bag = baggs.get(i);
if (soko.isBottomCollision(bag)) {
for (int j = 0; j < baggs.size(); j++) {
Baggage item = baggs.get(j);
if (!bag.equals(item)) {
if (bag.isBottomCollision(item)) {
return true;
}
}
if (checkWallCollision(bag,BOTTOM_COLLISION)) {
return true;
}
}
bag.move(0, SPACE);
isCompleted();
}
}
break;
default:
break;
}
return false;
}
public void isCompleted() {
int nOfBags = baggs.size();
int finishedBags = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nOfBags; i++) {
Baggage bag = baggs.get(i);
for (int j = 0; j < nOfBags; j++) {
Area area = areas.get(j);
if (bag.x() == area.x() && bag.y() == area.y()) {
finishedBags += 1;
}
}
}
if (finishedBags == nOfBags) {
isCompleted = true;
repaint();
}
}
public void restartLevel() {
areas.clear();
baggs.clear();
walls.clear();
initWorld();
if (isCompleted) {
isCompleted = false;
}
}
}
游戏简化了。 它仅提供非常基本的功能。 该代码比容易理解。 游戏只有一个关卡。
private final int OFFSET = 30;
private final int SPACE = 20;
private final int LEFT_COLLISION = 1;
private final int RIGHT_COLLISION = 2;
private final int TOP_COLLISION = 3;
private final int BOTTOM_COLLISION = 4;
墙图片大小为20x20像素。 这反映了SPACE常数。 OFFSET是窗口边界和游戏世界之间的距离。 有四种类型的碰撞。 每个数字都由一个数字常数表示。
private ArrayList<Wall> walls;
private ArrayList<Baggage> baggs;
private ArrayList<Area> areas;
墙壁,行李和区域是特殊的容器,可容纳游戏的所有墙壁,行李和区域。
private String level =
" ######\n"
+ " ## #\n"
+ " ##$ #\n"
+ " #### $##\n"
+ " ## $ $ #\n"
+ "#### # ## # ######\n"
+ "## # ## ##### ..#\n"
+ "## $ $ ..#\n"
+ "###### ### #@## ..#\n"
+ " ## #########\n"
+ " ########\n";
这是游戏的水平。 除空格外,还有五个字符。 井号(#)代表墙。 美元($)表示要移动的框。 点(.)字符表示我们必须移动框的位置。 at 字符(@)是推箱子。 最后,换行符(\n)开始了世界的新行。
private void initWorld() {
walls = new ArrayList<>();
baggs = new ArrayList<>();
areas = new ArrayList<>();
int x = OFFSET;
int y = OFFSET;
...
initWorld()方法启动游戏世界。 它遍历级别字符串并填充上述列表。
case '$':
b = new Baggage(x, y);
baggs.add(b);
x += SPACE;
break;
对于美元字符,我们创建一个Baggage对象。 该对象将附加到行李列表。 x 变量相应增加。
private void buildWorld(Graphics g) {
...
buildWorld()方法在窗口上绘制游戏世界。
ArrayList<Actor> world = new ArrayList<>();
world.addAll(walls);
world.addAll(areas);
world.addAll(baggs);
world.add(soko);
我们创建一个包含游戏所有对象的世界列表。
for (int i = 0; i < world.size(); i++) {
Actor item = world.get(i);
if (item instanceof Player || item instanceof Baggage) {
g.drawImage(item.getImage(), item.x() + 2, item.y() + 2, this);
} else {
g.drawImage(item.getImage(), item.x(), item.y(), this);
}
...
}
我们遍历世界容器并绘制对象。 播放器和行李图像稍小。 我们在其坐标上添加 2px 以使其居中。
if (isCompleted) {
g.setColor(new Color(0, 0, 0));
g.drawString("Completed", 25, 20);
}
如果完成该级别,则在窗口的左上角绘制"Completed"。
case KeyEvent.VK_LEFT:
if (checkWallCollision(soko,
LEFT_COLLISION)) {
return;
}
if (checkBagCollision(LEFT_COLLISION)) {
return;
}
soko.move(-SPACE, 0);
break;
在keyPressed()方法内部,我们检查了按下了哪些键。 我们用光标键控制推箱子对象。 如果按左光标键,我们将检查推箱子是否与墙壁或行李相撞。 如果没有,我们将推箱子向左移动。
case KeyEvent.VK_R:
restartLevel();
break;
如果按R键,我们将重新启动该级别。
case LEFT_COLLISION:
for (int i = 0; i < walls.size(); i++) {
Wall wall = walls.get(i);
if (actor.isLeftCollision(wall)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
创建checkWallCollision()方法以确保推箱子或行李不会通过墙壁。 有四种类型的碰撞。 上面几行检查是否有左碰撞。
private boolean checkBagCollision(int type) {
...
}
checkBagCollision()涉及更多。 行李可能会与墙壁,推箱子或其他行李发生碰撞。 仅当行李与推箱子碰撞且不与其他行李或墙壁碰撞时,才可以移动行李。 搬运行李时,该通过调用isCompleted()方法检查水平是否已完成。
for (int i = 0; i < nOfBags; i++) {
Baggage bag = baggs.get(i);
for (int j = 0; j < nOfBags; j++) {
Area area = areas.get(j);
if (bag.x() == area.x() && bag.y() == area.y()) {
finishedBags += 1;
}
}
}
isCompleted()方法检查级别是否完成。 我们得到行李数。 我们比较所有行李和目的地区域的 x 和 y 坐标。
if (finishedBags == nOfBags) {
isCompleted = true;
repaint();
}
当finishedBags变量等于游戏中的行李数时,游戏结束。
private void restartLevel() {
areas.clear();
baggs.clear();
walls.clear();
initWorld();
if (isCompleted) {
isCompleted = false;
}
}
如果我们做了一些不好的动作,我们可以重新启动关卡。 我们从列表中删除所有对象,然后再次启动世界。 isCompleted变量设置为false。
Actor.java
package com.zetcode;
import java.awt.Image;
public class Actor {
private final int SPACE = 20;
private int x;
private int y;
private Image image;
public Actor(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public Image getImage() {
return image;
}
public void setImage(Image img) {
image = img;
}
public int x() {
return x;
}
public int y() {
return y;
}
public void setX(int x) {
this.x = x;
}
public void setY(int y) {
this.y = y;
}
public boolean isLeftCollision(Actor actor) {
return x() - SPACE == actor.x() && y() == actor.y();
}
public boolean isRightCollision(Actor actor) {
return x() + SPACE == actor.x() && y() == actor.y();
}
public boolean isTopCollision(Actor actor) {
return y() - SPACE == actor.y() && x() == actor.x();
}
public boolean isBottomCollision(Actor actor) {
return y() + SPACE == actor.y() && x() == actor.x();
}
}
这是Actor类。 该类是游戏中其他演员的基础类。 它封装了推箱子游戏中对象的基本功能。
public boolean isLeftCollision(Actor actor) {
return x() - SPACE == actor.x() && y() == actor.y();
}
此方法检查演员是否与左侧的另一个演员(墙壁,行李,推箱子)相撞。
Wall.java
package com.zetcode;
import java.awt.Image;
import javax.swing.ImageIcon;
public class Wall extends Actor {
private Image image;
public Wall(int x, int y) {
super(x, y);
initWall();
}
private void initWall() {
ImageIcon iicon = new ImageIcon("src/resources/wall.png");
image = iicon.getImage();
setImage(image);
}
}
这是Wall类。 它继承自Actor类。 构建后,它将从资源中加载墙图像。
Player.java
package com.zetcode;
import java.awt.Image;
import javax.swing.ImageIcon;
public class Player extends Actor {
public Player(int x, int y) {
super(x, y);
initPlayer();
}
private void initPlayer() {
ImageIcon iicon = new ImageIcon("src/resources/sokoban.png");
Image image = iicon.getImage();
setImage(image);
}
public void move(int x, int y) {
int dx = x() + x;
int dy = y() + y;
setX(dx);
setY(dy);
}
}
这是Player类。
public void move(int x, int y) {
int dx = x() + x;
int dy = y() + y;
setX(dx);
setY(dy);
}
move()方法将对象移动到世界内部。
Baggage.java
package com.zetcode;
import java.awt.Image;
import javax.swing.ImageIcon;
public class Baggage extends Actor {
public Baggage(int x, int y) {
super(x, y);
initBaggage();
}
private void initBaggage() {
ImageIcon iicon = new ImageIcon("src/resources/baggage.png");
Image image = iicon.getImage();
setImage(image);
}
public void move(int x, int y) {
int dx = x() + x;
int dy = y() + y;
setX(dx);
setY(dy);
}
}
这是Baggage对象的类。 该对象是可移动的,因此也具有move()方法。
Area.java
package com.zetcode;
import java.awt.Image;
import javax.swing.ImageIcon;
public class Area extends Actor {
public Area(int x, int y) {
super(x, y);
initArea();
}
private void initArea() {
ImageIcon iicon = new ImageIcon("src/resources/area.png");
Image image = iicon.getImage();
setImage(image);
}
}
这是Area类。 这是我们尝试放置行李的对象。
Sokoban.java
package com.zetcode;
import java.awt.EventQueue;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
public class Sokoban extends JFrame {
private final int OFFSET = 30;
public Sokoban() {
initUI();
}
private void initUI() {
Board board = new Board();
add(board);
setTitle("Sokoban");
setSize(board.getBoardWidth() + OFFSET,
board.getBoardHeight() + 2 * OFFSET);
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
setLocationRelativeTo(null);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> {
Sokoban game = new Sokoban();
game.setVisible(true);
});
}
}
这是主要的类。
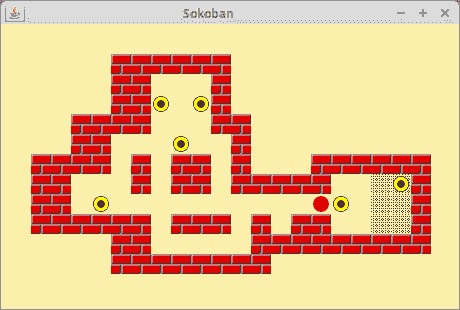
图:推箱子
这是推箱子游戏。

