Java SWT 中的布局管理
在本章中,我们将展示如何在窗口或对话框中布置窗口小部件。
在设计应用的 GUI 时,我们决定使用哪些小部件以及如何在应用中组织这些小部件。 为了组织小部件,我们使用称为布局容器的专用非可见小部件。
Composite是用于放置子窗口小部件的容器。 Composite的布局管理器是通过setLayout()方法设置的。 Shell也是Composite。 它没有默认的布局管理器,在这种情况下,将使用绝对定位来放置小部件。
SWT 具有以下标准布局类:
FillLayoutRowLayoutFormLayoutGridLayout
FillLayout在单个行或列中布置大小相等的小部件。 RowLayout在行或列中布置小部件,并具有填充,环绕和间距选项。 FormLayout通过为小部件的每一侧创建附件来布局小部件。 GridLayout将小部件布置在网格中。
布局类可以具有对应的布局数据类,其中包含特定子项的布局数据。 例如,RowLayout具有名为RowData的布局数据类,GridLayout具有GridData,而FormLayout具有FormData。
绝对定位
在大多数情况下,程序员应使用布局管理器。 在某些情况下,我们也可以使用绝对定位。 在绝对定位中,程序员以像素为单位指定每个小部件的位置和大小。 如果我们调整窗口大小,则小部件的大小和位置不会改变。 在各种平台上,应用看起来都不同,在 Linux 上看起来不错,在 Mac OS 上看起来不太正常。 在应用中更改字体可能会破坏布局。 如果我们将应用翻译成另一种语言,则必须重做布局。 对于所有这些问题,仅在有理由的情况下才使用绝对定位,或者您的应用是简单的测试。
绝对定位是通过setSize(),setLocation()和setBounds()方法完成的。
AbsoluteLayoutEx.java
package com.zetcode;
import org.eclipse.swt.SWT;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Button;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Display;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Shell;
/**
* ZetCode Java SWT tutorial
*
* In this program, we position two
* buttons using absolute coordinates.
*
* Author: Jan Bodnar
* Website: zetcode.com
* Last modified: June 2015
*/
public class AbsoluteLayoutEx {
public AbsoluteLayoutEx(Display display) {
initUI(display);
}
private void initUI(Display display) {
Shell shell = new Shell(display, SWT.SHELL_TRIM | SWT.CENTER);
Button btn1 = new Button(shell, SWT.PUSH);
btn1.setText("Button");
btn1.setBounds(20, 50, 80, 30);
Button btn2 = new Button(shell, SWT.PUSH);
btn2.setText("Button");
btn2.setSize(80, 30);
btn2.setLocation(50, 100);
shell.setText("Absolute layout");
shell.setSize(300, 250);
shell.open();
while (!shell.isDisposed()) {
if (!display.readAndDispatch()) {
display.sleep();
}
}
}
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
public static void main(String[] args) {
Display display = new Display();
AbsoluteLayoutEx ex = new AbsoluteLayoutEx(display);
display.dispose();
}
}
在我们的示例中,我们使用绝对定位在窗口上放置了两个按钮。
btn1.setBounds(20, 50, 80, 30);
setBounds()方法有两件事:将按钮定位在x = 20和y = 50,并将按钮的大小设置为width = 80和height = 30。
button2.setSize(80, 30);
button2.setLocation(50, 100);
在这里,我们分两个步骤进行相同的操作。 首先,我们使用setSize()方法调整按钮的大小。 然后,我们使用setLocation()方法将其定位在窗口上。
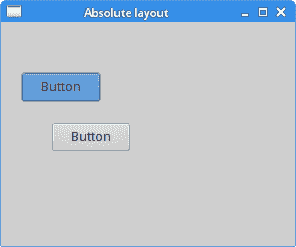
图:绝对布局
FillLayout管理器
FillLayout是最简单的布局类。 它将小部件布置在一行或一列中,迫使它们具有相同的大小。
FillLayoutEx.java
package com.zetcode;
import org.eclipse.swt.SWT;
import org.eclipse.swt.graphics.Device;
import org.eclipse.swt.graphics.Image;
import org.eclipse.swt.graphics.Rectangle;
import org.eclipse.swt.layout.FillLayout;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Display;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Label;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Shell;
/**
* ZetCode Java SWT tutorial
*
* This program demonstrates the FillLayout
* manager
*
* Author: Jan Bodnar
* Website: zetcode.com
* Last modified: May 2015
*/
public class FillLayoutEx {
private Image castle;
public FillLayoutEx(Display display) {
initUI(display);
}
private void initUI(Display display) {
Shell shell = new Shell(display, SWT.SHELL_TRIM | SWT.CENTER);
shell.setLayout(new FillLayout());
loadImage(shell);
Label label = new Label(shell, SWT.IMAGE_PNG);
label.setImage(castle);
shell.setText("FillLayout");
Rectangle rect = castle.getBounds();
shell.setSize(rect.width, rect.height);
shell.open();
while (!shell.isDisposed()) {
if (!display.readAndDispatch()) {
display.sleep();
}
}
}
private void loadImage(Shell shell) {
Device dev = shell.getDisplay();
try {
castle = new Image(dev, "redrock.png");
} catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println("Cannot load image");
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
System.exit(1);
}
}
@Override
public void finalize() {
castle.dispose();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Display display = new Display();
FillLayoutEx app = new FillLayoutEx(display);
app.finalize();
display.dispose();
}
}
在我们的示例中,我们使用此管理器显示图像。
shell.setLayout(new FillLayout());
我们将FillLayout设置为外壳的布局类。 使用setLayout()方法设置布局。
Rectangle rect = castle.getBounds();
shell.setSize(rect.width, rect.height);
我们找出图片的大小来调整外壳的大小,以完全适合图像的大小。
Label label = new Label(shell, SWT.IMAGE_PNG);
label.setImage(castle);
我们将图像设置为标签小部件。
private void loadImage(Shell shell) {
Device dev = shell.getDisplay();
try {
castle = new Image(dev, "redrock.png");
} catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println("Cannot load image");
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
System.exit(1);
}
}
loadImage()方法从磁盘加载图像。

图:FillLayout
RowLayout
RowLayout管理器将所有小部件放置在一行或一列中。
RowLayoutEx.java
package com.zetcode;
import org.eclipse.swt.SWT;
import org.eclipse.swt.layout.RowData;
import org.eclipse.swt.layout.RowLayout;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Button;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Display;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Shell;
/**
* ZetCode Java SWT tutorial
*
* This program demonstrates the RowLayout
* manager.
*
* Author: Jan Bodnar
* Website: zetcode.com
* Last modified: June 2015
*/
public class RowLayoutEx {
public RowLayoutEx(Display display) {
initUI(display);
}
private void initUI(Display display) {
Shell shell = new Shell(display, SWT.SHELL_TRIM | SWT.CENTER);
RowLayout rowLayout = new RowLayout(SWT.HORIZONTAL);
rowLayout.marginTop = 10;
rowLayout.marginBottom = 10;
rowLayout.marginLeft = 5;
rowLayout.marginRight = 5;
rowLayout.spacing = 10;
shell.setLayout(rowLayout);
Button btn1 = new Button(shell, SWT.PUSH);
btn1.setText("Button");
btn1.setLayoutData(new RowData(80, 30));
Button btn2 = new Button(shell, SWT.PUSH);
btn2.setText("Button");
btn2.setLayoutData(new RowData(80, 30));
Button btn3 = new Button(shell, SWT.PUSH);
btn3.setText("Button");
btn3.setLayoutData(new RowData(80, 30));
shell.setText("RowLayout");
shell.pack();
shell.open();
while (!shell.isDisposed()) {
if (!display.readAndDispatch()) {
display.sleep();
}
}
}
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
public static void main(String[] args) {
Display display = new Display();
RowLayoutEx ex = new RowLayoutEx(display);
display.dispose();
}
}
在我们的示例中,我们创建了三个按钮的行。
RowLayout rowLayout = new RowLayout(SWT.HORIZONTAL);
将创建水平RowLayout。 这些小部件将放置在一行中。
rowLayout.marginTop = 10;
rowLayout.marginBottom = 10;
rowLayout.marginLeft = 5;
rowLayout.marginRight = 5;
边距指定沿容器边缘的空间。
rowLayout.spacing = 10;
spacing属性指定按钮之间的间距。
shell.setLayout(rowLayout);
我们将行布局指定为外壳布局。
Button btn1 = new Button(shell, SWT.PUSH);
btn1.setText("Button");
btn1.setLayoutData(new RowData(80, 30));
创建了Button。 setLayoutData()指定按钮的大小。
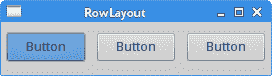
图:RowLayout管理器
按钮
在最后一个示例中,我们使用FormLayout管理器创建一个示例。 该管理器使用两个对象FormData和FormAttachment控制子项的位置和大小。
ButtonsEx.java
package com.zetcode;
import org.eclipse.swt.SWT;
import org.eclipse.swt.layout.FormAttachment;
import org.eclipse.swt.layout.FormData;
import org.eclipse.swt.layout.FormLayout;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Button;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Display;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Shell;
/**
* ZetCode Java SWT tutorial
*
* In this program, we position two buttons
* in the bottom right corner of the window.
*
* Author: Jan Bodnar
* Website: zetcode.com
* Last modified: May 2015
*/
public class ButtonsEx {
public ButtonsEx(Display display) {
initUI(display);
}
private void initUI(Display display) {
Shell shell = new Shell(display, SWT.SHELL_TRIM | SWT.CENTER);
FormLayout layout = new FormLayout();
shell.setLayout(layout);
Button okBtn = new Button(shell, SWT.PUSH);
okBtn.setText("OK");
Button cancBtn = new Button(shell, SWT.PUSH);
cancBtn.setText("Cancel");
FormData cancelData = new FormData(80, 30);
cancelData.right = new FormAttachment(98);
cancelData.bottom = new FormAttachment(95);
cancBtn.setLayoutData(cancelData);
FormData okData = new FormData(80, 30);
okData.right = new FormAttachment(cancBtn, -5, SWT.LEFT);
okData.bottom = new FormAttachment(cancBtn, 0, SWT.BOTTOM);
okBtn.setLayoutData(okData);
shell.setText("Buttons");
shell.setSize(350, 200);
shell.open();
while (!shell.isDisposed()) {
if (!display.readAndDispatch()) {
display.sleep();
}
}
}
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
public static void main(String[] args) {
Display display = new Display();
ButtonsEx ex = new ButtonsEx(display);
display.dispose();
}
}
在此代码示例中,我们在窗口的右下角放置了两个按钮。
FormLayout layout = new FormLayout();
shell.setLayout(layout);
FormLayout管理器已创建。
Button okBtn = new Button(shell, SWT.PUSH);
okBtn.setText("OK");
Button cancBtn = new Button(shell, SWT.PUSH);
cancBtn.setText("Cancel");
创建两个按钮并将其设置到外壳。
FormData cancelData = new FormData(80, 30);
取消按钮的大小为80x30。
cancelData.right = new FormAttachment(98);
cancelData.bottom = new FormAttachment(95);
按钮的右侧附着在窗口宽度的 98% 处。 按钮的底部固定在窗口高度的 95% 处。
okData.right = new FormAttachment(cancelButton, -5, SWT.LEFT);
okData.bottom = new FormAttachment(cancelButton, 0, SWT.BOTTOM);
“确定”按钮的右侧位于“取消”按钮的左侧 5 像素处。 “确定”按钮的底部与“取消”按钮的底部对齐。
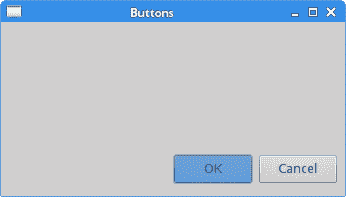
图:按钮
新建文件夹
在下面的示例中,我们使用FormLayout和RowLayout管理器创建窗口布局。
NewFolderEx.java
package com.zetcode;
import org.eclipse.swt.SWT;
import org.eclipse.swt.layout.FormAttachment;
import org.eclipse.swt.layout.FormData;
import org.eclipse.swt.layout.FormLayout;
import org.eclipse.swt.layout.RowData;
import org.eclipse.swt.layout.RowLayout;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Button;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Composite;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Display;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Label;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Shell;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Text;
/**
* ZetCode Java SWT tutorial
*
* This program creates a layout using a
* FormLayout and a RowLayout.
*
* Author: Jan Bodnar
* Website: zetcode.com
* Last modified: June 2015
*/
public class NewFolderEx {
public NewFolderEx(Display display) {
initUI(display);
}
private void initUI(Display display) {
Shell shell = new Shell(display, SWT.SHELL_TRIM | SWT.CENTER);
shell.setLayout(new FormLayout());
Label lbl = new Label(shell, SWT.LEFT);
lbl.setText("Name:");
FormData data1 = new FormData();
data1.left = new FormAttachment(0, 5);
data1.top = new FormAttachment(0, 10);
lbl.setLayoutData(data1);
Text text = new Text(shell, SWT.SINGLE);
FormData data2 = new FormData();
data2.left = new FormAttachment(lbl, 15);
data2.top = new FormAttachment(0, 10);
data2.right = new FormAttachment(100, -5);
text.setLayoutData(data2);
Composite com = new Composite(shell, SWT.NONE);
RowLayout rowLayout = new RowLayout();
com.setLayout(rowLayout);
Button okBtn = new Button(com, SWT.PUSH);
okBtn.setText("OK");
okBtn.setLayoutData(new RowData(80, 30));
Button closeBtn = new Button(com, SWT.PUSH);
closeBtn.setText("Close");
closeBtn.setLayoutData(new RowData(80, 30));
FormData data3 = new FormData();
data3.bottom = new FormAttachment(100, -5);
data3.right = new FormAttachment(100, 0);
com.setLayoutData(data3);
Text mainText = new Text(shell, SWT.MULTI | SWT.BORDER);
FormData data4 = new FormData();
data4.width = 250;
data4.height = 180;
data4.top = new FormAttachment(text, 10);
data4.left = new FormAttachment(0, 5);
data4.right = new FormAttachment(100, -5);
data4.bottom = new FormAttachment(com, -10);
mainText.setLayoutData(data4);
shell.setText("New folder");
shell.pack();
shell.open();
while (!shell.isDisposed()) {
if (!display.readAndDispatch())
display.sleep();
}
}
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
public static void main(String[] args) {
Display display = new Display();
NewFolderEx ex = new NewFolderEx(display);
display.dispose();
}
}
在示例中,有标签,文本和按钮小部件。
Shell shell = new Shell(display, SWT.SHELL_TRIM | SWT.CENTER);
shell.setLayout(new FormLayout());
FormLayout设置为外壳的主布局管理器。
Label lbl = new Label(shell, SWT.LEFT);
lbl.setText("Name:");
FormData data1 = new FormData();
data1.left = new FormAttachment(0, 5);
data1.top = new FormAttachment(0, 10);
lbl.setLayoutData(data1);
标签窗口小部件附在窗口的左上角。
Text text = new Text(shell, SWT.SINGLE);
FormData data2 = new FormData();
data2.left = new FormAttachment(lbl, 15);
data2.top = new FormAttachment(0, 10);
data2.right = new FormAttachment(100, -5);
text.setLayoutData(data2);
在标签旁边,我们放置一个Text控件。 文本控件的左侧相对于标签放置。
Composite com = new Composite(shell, SWT.NONE);
RowLayout rowLayout = new RowLayout();
com.setLayout(rowLayout);
创建一个Composite并将其设置为RowLayout管理器。 这两个按钮进入该容器。 将RowLayout用于按钮要比直接通过FormLayout进行组织要容易一些。
Button okBtn = new Button(com, SWT.PUSH);
okBtn.setText("OK");
okBtn.setLayoutData(new RowData(80, 30));
Button closeBtn = new Button(com, SWT.PUSH);
closeBtn.setText("Close");
closeBtn.setLayoutData(new RowData(80, 30));
创建两个按钮。 他们的父部件是Composite。
FormData data3 = new FormData();
data3.bottom = new FormAttachment(100, -5);
data3.right = new FormAttachment(100, 0);
com.setLayoutData(data3);
Composite本身与FormLayout一起放置在窗口的底部。 负值是与相邻小部件或窗口边界的偏移量。
Text mainText = new Text(shell, SWT.MULTI | SWT.BORDER);
FormData data4 = new FormData();
data4.width = 250;
data4.height = 180;
data4.top = new FormAttachment(text, 10);
data4.left = new FormAttachment(0, 5);
data4.right = new FormAttachment(100, -5);
data4.bottom = new FormAttachment(com, -10);
mainText.setLayoutData(data4);
最后,创建了Text主窗口小部件。 它占用了大部分窗口区域。 width和height属性指定控件的初始首选大小。
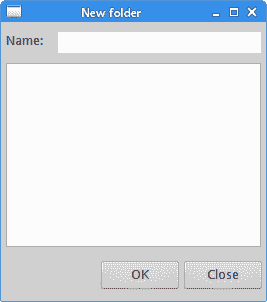
图:新文件夹
GridLayout
GridLayout管理器将其子窗口小部件放入网格中。
GridLayoutEx.java
package com.zetcode;
import org.eclipse.swt.SWT;
import org.eclipse.swt.graphics.Color;
import org.eclipse.swt.layout.GridData;
import org.eclipse.swt.layout.GridLayout;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Display;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Label;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Shell;
/**
* ZetCode Java SWT tutorial
*
* This example presents the GridLayout.
*
* Author: Jan Bodnar
* Website: zetcode.com
* Last modified: June 2015
*/
public class GridLayoutEx {
public GridLayoutEx(Display display) {
initUI(display);
}
private void initUI(Display display) {
Shell shell = new Shell(display, SWT.SHELL_TRIM | SWT.CENTER);
Color col = new Color(display, 100, 200, 100);
shell.setBackground(col);
col.dispose();
GridLayout layout = new GridLayout(2, false);
shell.setLayout(layout);
Label lbl1 = new Label(shell, SWT.NONE);
GridData gd1 = new GridData(SWT.FILL, SWT.FILL, true, true);
lbl1.setLayoutData(gd1);
Color col1 = new Color(display, 250, 155, 100);
lbl1.setBackground(col1);
col1.dispose();
Label lbl2 = new Label(shell, SWT.NONE);
GridData gd2 = new GridData(SWT.FILL, SWT.FILL, true, true);
gd2.heightHint = 100;
lbl2.setLayoutData(gd2);
Color col2 = new Color(display, 10, 155, 100);
lbl2.setBackground(col2);
col2.dispose();
Label lbl3 = new Label(shell, SWT.NONE);
GridData gd3 = new GridData(SWT.FILL, SWT.FILL, true, true);
gd3.widthHint = 300;
gd3.heightHint = 100;
gd3.horizontalSpan = 2;
lbl3.setLayoutData(gd3);
Color col3 = new Color(display, 100, 205, 200);
lbl3.setBackground(col3);
col3.dispose();
shell.setText("Grid");
shell.pack();
shell.open();
while (!shell.isDisposed()) {
if (!display.readAndDispatch())
display.sleep();
}
}
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
public static void main(String[] args) {
Display display = new Display();
GridLayoutEx ex = new GridLayoutEx(display);
display.dispose();
}
}
在示例中,我们在网格中放置了三个标签。 每个标签具有不同的背景色。
Color col = new Color(display, 100, 200, 100);
shell.setBackground(col);
col.dispose();
setBackground()方法为外壳设置背景色。
GridLayout layout = new GridLayout(2, false);
shell.setLayout(layout);
实例化GridLayout管理器并将其设置为外壳的布局管理器。 网格由 2 列组成。
Label lbl1 = new Label(shell, SWT.NONE);
GridData gd1 = new GridData(SWT.FILL, SWT.FILL, true, true);
lbl1.setLayoutData(gd1);
第一个标签进入网格的左上角单元格。 GridData类的四个参数使标签组件填充其单元格并在两个方向上扩展。
Label lbl2 = new Label(shell, SWT.NONE);
GridData gd2 = new GridData(SWT.FILL, SWT.FILL, true, true);
gd2.heightHint = 100;
lbl2.setLayoutData(gd2);
第二个标签转到相邻的单元格。 heightHint属性指定标签的首选高度。 请注意,它也会影响先前的窗口小部件,因为该属性有效地设置了行的首选高度。
Label lbl3 = new Label(shell, SWT.NONE);
GridData gd3 = new GridData(SWT.FILL, SWT.FILL, true, true);
gd3.widthHint = 300;
gd3.heightHint = 100;
gd3.horizontalSpan = 2;
lbl3.setLayoutData(gd3);
第三个标签进入第二行。 horizontalSpan属性使标签跨越两列。
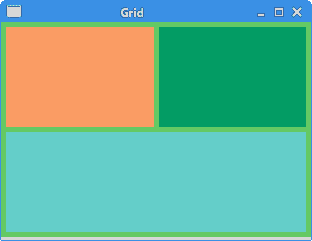
图:简单 GridLayout
计算器
在下面的示例中,我们使用GridLayout管理器创建计算器的框架。
CalculatorEx.java
package com.zetcode;
import org.eclipse.swt.SWT;
import org.eclipse.swt.layout.GridData;
import org.eclipse.swt.layout.GridLayout;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Button;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Display;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Label;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Shell;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Text;
/**
* ZetCode Java SWT tutorial
*
* In this program, we use the GridLayout to
* create a calculator skeleton.
*
* Author: Jan Bodnar
* Website: zetcode.com
* Last modified: June 2015
*/
public class CalculatorEx {
public CalculatorEx(Display display) {
initUI(display);
}
private void initUI(Display display) {
Shell shell = new Shell(display, SWT.DIALOG_TRIM | SWT.CENTER);
GridLayout gl = new GridLayout(4, true);
gl.marginHeight = 5;
shell.setLayout(gl);
String[] buttons = {
"Cls", "Bck", "", "Close", "7", "8", "9", "/", "4",
"5", "6", "*", "1", "2", "3", "-", "0", ".", "=", "+"
};
Text text = new Text(shell, SWT.SINGLE);
GridData gridData = new GridData();
gridData.horizontalSpan = 4;
gridData.horizontalAlignment = GridData.FILL;
text.setLayoutData(gridData);
for (int i = 0; i < buttons.length; i++) {
if (i == 2) {
Label lbl = new Label(shell, SWT.CENTER);
GridData gd = new GridData(SWT.FILL, SWT.FILL, false, false);
lbl.setLayoutData(gd);
} else {
Button btn = new Button(shell, SWT.PUSH);
btn.setText(buttons[i]);
GridData gd = new GridData(SWT.FILL, SWT.FILL, false, false);
gd.widthHint = 50;
gd.heightHint = 30;
btn.setLayoutData(gd);
}
}
shell.setText("Calculator");
shell.pack();
shell.open();
while (!shell.isDisposed()) {
if (!display.readAndDispatch()) {
display.sleep();
}
}
}
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
public static void main(String[] args) {
Display display = new Display();
CalculatorEx ex = new CalculatorEx(display);
display.dispose();
}
}
我们使用GridLayout管理器创建计算器的框架。 我们使用三种类型的小部件:文本小部件,标签小部件和几个按钮。
Shell shell = new Shell(display, SWT.DIALOG_TRIM | SWT.CENTER);
使用SWT.DIALOG_TRIM标志,使窗口不可调整大小。
GridLayout gl = new GridLayout(4, true);
gl.marginHeight = 5;
shell.setLayout(gl);
我们创建一个具有 4 列的GridLayout,并提供顶部和底部页边距。
Text text = new Text(shell, SWT.SINGLE);
GridData gridData = new GridData();
gridData.horizontalSpan = 4;
gridData.horizontalAlignment = GridData.FILL;
text.setLayoutData(gridData);
GridData是与GridLayout关联的布局数据对象。 使用horizontalSpan属性,我们使文本小部件跨越所有四列。 设置为GridData.FILL的horizontalAlignment使文本窗口小部件填充布局管理器分配给它的整个区域。
Button btn = new Button(shell, SWT.PUSH);
btn.setText(buttons[i]);
GridData gd = new GridData(SWT.FILL, SWT.FILL, false, false);
gd.widthHint = 50;
gd.heightHint = 30;
btn.setLayoutData(gd);
在for循环内,我们创建按钮并将其放入网格中。 通过widthHint和heightHint属性,我们可以设置按钮的首选大小。
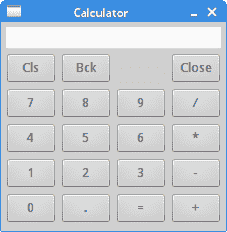
图:计算机骨架
在 Java SWT 教程的这一部分中,我们讨论了小部件的布局管理。

