Qt5 中的布局管理
在 Qt5 编程教程的这一部分中,我们将讨论小部件的布局管理。 我们提到了QHBoxLayout,QVBoxLayout,QFormLayout和QGridLayout管理器。
典型的应用由各种小部件组成。 这些小部件放置在布局内。 程序员必须管理应用的布局。 在 Qt5 中,我们有两个选择:
- 绝对定位
- 布局管理器
绝对定位
程序员以像素为单位指定每个小部件的位置和大小。 当使用绝对定位时,我们必须了解几件事。
- 如果我们调整窗口大小,则小部件的大小和位置不会改变。
- 在各种平台上,应用看起来有所不同(通常很差)。
- 在我们的应用中更改字体可能会破坏布局。
- 如果决定更改布局,则必须完全重做布局,这既繁琐又耗时。
在某些情况下,我们可能会使用绝对定位。 但是大多数情况下,在实际程序中,程序员使用布局管理器。
absolute.cpp
#include <QApplication>
#include <QDesktopWidget>
#include <QTextEdit>
class Absolute : public QWidget {
public:
Absolute(QWidget *parent = 0);
};
Absolute::Absolute(QWidget *parent)
: QWidget(parent) {
QTextEdit *ledit = new QTextEdit(this);
ledit->setGeometry(5, 5, 200, 150);
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
QApplication app(argc, argv);
Absolute window;
window.setWindowTitle("Absolute");
window.show();
return app.exec();
}
setGeometry()方法用于以绝对坐标将窗口小部件放置在窗口上。
QTextEdit *edit = new QTextEdit(this);
ledit->setGeometry(5, 5, 200, 150);
我们创建一个QTextEdit小部件并手动定位。 setGeometry()方法有两件事:将窗口小部件定位到绝对坐标并调整窗口小部件的大小。
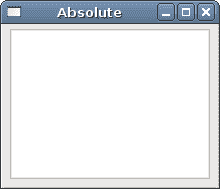
图:调整大小前
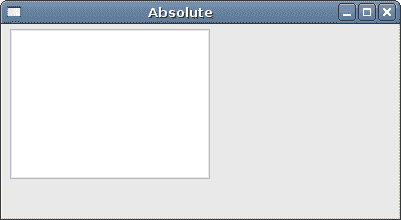
图:调整大小后
QVBoxLayout
QVBoxLayout类垂直排列小部件。 使用addWidget()方法将小部件添加到布局。
verticalbox.h
#pragma once
#include <QWidget>
class VerticalBox : public QWidget {
public:
VerticalBox(QWidget *parent = 0);
};
头文件。
verticalbox.cpp
#include "verticalbox.h"
#include <QVBoxLayout>
#include <QPushButton>
VerticalBox::VerticalBox(QWidget *parent)
: QWidget(parent) {
QVBoxLayout *vbox = new QVBoxLayout(this);
vbox->setSpacing(1);
QPushButton *settings = new QPushButton("Settings", this);
settings->setSizePolicy(QSizePolicy::Expanding, QSizePolicy::Expanding);
QPushButton *accounts = new QPushButton("Accounts", this);
accounts->setSizePolicy(QSizePolicy::Expanding, QSizePolicy::Expanding);
QPushButton *loans = new QPushButton("Loans", this);
loans->setSizePolicy(QSizePolicy::Expanding, QSizePolicy::Expanding);
QPushButton *cash = new QPushButton("Cash", this);
cash->setSizePolicy(QSizePolicy::Expanding, QSizePolicy::Expanding);
QPushButton *debts = new QPushButton("Debts", this);
debts->setSizePolicy(QSizePolicy::Expanding, QSizePolicy::Expanding);
vbox->addWidget(settings);
vbox->addWidget(accounts);
vbox->addWidget(loans);
vbox->addWidget(cash);
vbox->addWidget(debts);
setLayout(vbox);
}
在我们的示例中,我们有一个垂直布局管理器。 我们在其中放入了五个按钮。 我们使所有按钮都可以在两个方向上展开。
QVBoxLayout *vbox = new QVBoxLayout(this);
vbox->setSpacing(1);
我们创建QVBoxLayout并在子窗口小部件之间设置 1px 的间距。
QPushButton *settings = new QPushButton("Settings", this);
settings->setSizePolicy(QSizePolicy::Expanding, QSizePolicy::Expanding);
我们创建一个按钮并为其设置大小策略。 子窗口小部件由布局管理器管理。 默认情况下,按钮水平扩展,垂直方向固定大小。 如果要更改它,我们将设置一个新的大小策略。 在我们的例子中,按钮可以向两个方向扩展。
vbox->addWidget(settings);
vbox->addWidget(accounts);
...
我们使用addWidget()方法将子窗口小部件添加到布局管理器。
setLayout(vbox);
我们为窗口设置QVBoxLayout管理器。
main.cpp
#include "verticalbox.h"
#include <QApplication>
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
QApplication app(argc, argv);
VerticalBox window;
window.resize(240, 230);
window.setWindowTitle("VerticalBox");
window.show();
return app.exec();
}
主文件。
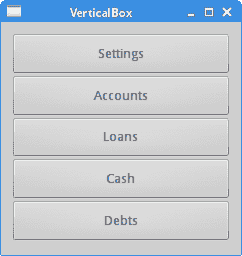
图:QVBoxLayout
按钮
在下面的示例中,我们在窗口的客户区域上显示两个按钮。 它们将位于窗口的右下角。
buttons.h
#pragma once
#include <QWidget>
#include <QPushButton>
class Buttons : public QWidget {
public:
Buttons(QWidget *parent = 0);
private:
QPushButton *okBtn;
QPushButton *applyBtn;
};
头文件。
buttons.cpp
#include "buttons.h"
#include <QVBoxLayout>
#include <QHBoxLayout>
Buttons::Buttons(QWidget *parent)
: QWidget(parent) {
QVBoxLayout *vbox = new QVBoxLayout(this);
QHBoxLayout *hbox = new QHBoxLayout();
okBtn = new QPushButton("OK", this);
applyBtn = new QPushButton("Apply", this);
hbox->addWidget(okBtn, 1, Qt::AlignRight);
hbox->addWidget(applyBtn, 0);
vbox->addStretch(1);
vbox->addLayout(hbox);
}
假设我们想在窗口的右下角有两个按钮。
QVBoxLayout *vbox = new QVBoxLayout(this);
QHBoxLayout *hbox = new QHBoxLayout();
我们创建了两个框布局管理器:一个垂直框布局管理器和一个水平框布局管理器。
okBtn = new QPushButton("OK", this);
applyBtn = new QPushButton("Apply", this);
我们创建两个按钮。
hbox->addWidget(okBtn, 1, Qt::AlignRight);
hbox->addWidget(applyBtn, 0);
这些按钮位于水平布局管理器中。 使用addWidget()方法。 这些按钮右对齐。 第一个参数是子窗口小部件。 第二个参数是拉伸因子,最后一个参数是对齐。 通过将“确定”按钮的拉伸因子设置为 1,我们在窗口的左侧到右侧留出一定的空间。 窗口小部件不会扩展到分配给它的所有空间。 最后,Qt::AlignRight常数将小部件对齐到分配空间的右侧。
vbox->addStretch(1);
vbox->addLayout(hbox);
通过调用addStretch()方法,我们在垂直框中放入了一个可扩展的空白区域。 然后,将水平框布局添加到垂直框布局。
main.cpp
#include <QApplication>
#include "buttons.h"
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
QApplication app(argc, argv);
Buttons window;
window.resize(290, 170);
window.setWindowTitle("Buttons");
window.show();
return app.exec();
}
主文件。
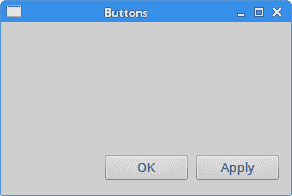
图:按钮
嵌套布局
以下示例的目的是说明可以合并布局管理器。 通过甚至简单布局的组合,我们可以创建复杂的对话框或窗口。 要嵌套布局,我们利用addLayout()方法。
nesting.h
#pragma once
#include <QWidget>
class Layouts : public QWidget {
public:
Layouts(QWidget *parent = 0);
};
这是头文件。
nesting.cpp
#include <QVBoxLayout>
#include <QPushButton>
#include <QListWidget>
#include "nesting.h"
Layouts::Layouts(QWidget *parent)
: QWidget(parent) {
QVBoxLayout *vbox = new QVBoxLayout();
QHBoxLayout *hbox = new QHBoxLayout(this);
QListWidget *lw = new QListWidget(this);
lw->addItem("The Omen");
lw->addItem("The Exorcist");
lw->addItem("Notes on a scandal");
lw->addItem("Fargo");
lw->addItem("Capote");
QPushButton *add = new QPushButton("Add", this);
QPushButton *rename = new QPushButton("Rename", this);
QPushButton *remove = new QPushButton("Remove", this);
QPushButton *removeall = new QPushButton("Remove All", this);
vbox->setSpacing(3);
vbox->addStretch(1);
vbox->addWidget(add);
vbox->addWidget(rename);
vbox->addWidget(remove);
vbox->addWidget(removeall);
vbox->addStretch(1);
hbox->addWidget(lw);
hbox->addSpacing(15);
hbox->addLayout(vbox);
setLayout(hbox);
}
在示例中,我们创建一个窗口,该窗口由四个按钮和一个列表小部件组成。 这些按钮被分组在一个垂直列中,并位于列表小部件的右侧。 如果我们调整窗口的大小,列表小部件也将被调整大小。
QVBoxLayout *vbox = new QVBoxLayout();
QVBoxLayout将是按钮的列。
QHBoxLayout *hbox = new QHBoxLayout(this);
QHBoxLayout将是小部件的基本布局。
QListWidget *lw = new QListWidget(this);
lw->addItem("The Omen");
lw->addItem("The Exorcist");
lw->addItem("Notes on a scandal");
lw->addItem("Fargo");
lw->addItem("Capote");
QListWidget已创建。
QPushButton *add = new QPushButton("Add", this);
QPushButton *rename = new QPushButton("Rename", this);
QPushButton *remove = new QPushButton("Remove", this);
QPushButton *removeall = new QPushButton("Remove All", this);
在这里,我们创建四个按钮。
vbox->setSpacing(3);
vbox->addStretch(1);
vbox->addWidget(add);
vbox->addWidget(rename);
vbox->addWidget(remove);
vbox->addWidget(removeall);
vbox->addStretch(1);
创建带有四个按钮的垂直框。 我们在按钮之间留了一些空间。 注意,我们在垂直框的顶部和底部添加了一个拉伸因子。 这样,按钮可以垂直居中。
hbox->addWidget(lw);
hbox->addSpacing(15);
hbox->addLayout(vbox);
列表小部件和按钮的垂直框放置在水平框布局中。 addLayout()方法用于将一个布局添加到另一个布局。
setLayout(hbox);
我们为父窗口设置基本布局。
main.cpp
#include <QApplication>
#include "nesting.h"
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
QApplication app(argc, argv);
Layouts window;
window.setWindowTitle("Layouts");
window.show();
return app.exec();
}
这是主文件。
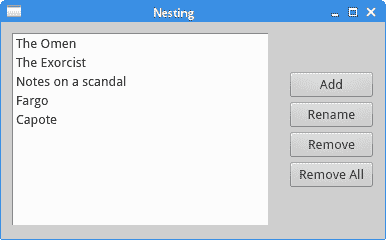
图:嵌套布局
QFormLayout
QFormLayout是一个简单的布局管理器,用于管理输入窗口小部件及其相关标签的形式。 它以两列的形式布置其子项。 左列包含标签,右列包含输入窗口小部件,例如QLineEdit或QSpinBox。
form.h
#pragma once
#include <QWidget>
class FormEx : public QWidget {
public:
FormEx(QWidget *parent = 0);
};
这是标题文件管理器。
form.cpp
#include <QFormLayout>
#include <QLabel>
#include <QLineEdit>
#include "form.h"
FormEx::FormEx(QWidget *parent)
: QWidget(parent) {
QLineEdit *nameEdit = new QLineEdit(this);
QLineEdit *addrEdit = new QLineEdit(this);
QLineEdit *occpEdit = new QLineEdit(this);
QFormLayout *formLayout = new QFormLayout;
formLayout->setLabelAlignment(Qt::AlignRight | Qt::AlignVCenter);
formLayout->addRow("Name:", nameEdit);
formLayout->addRow("Email:", addrEdit);
formLayout->addRow("Age:", occpEdit);
setLayout(formLayout);
}
该示例创建一个包含三个标签和三个行编辑的表单。
QFormLayout *formLayout = new QFormLayout;
创建QFormLayout的实例。
formLayout->setLabelAlignment(Qt::AlignRight | Qt::AlignVCenter);
使用setLabelAlignment()方法,我们设置标签小部件的对齐方式。
formLayout->addRow("Name:", nameEdit);
addRow()方法将新行添加到表单布局的底部,并带有给定的标签和输入小部件。
main.cpp
#include <QApplication>
#include "form.h"
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
QApplication app(argc, argv);
FormEx window;
window.setWindowTitle("Form example");
window.show();
return app.exec();
}
这是主文件。
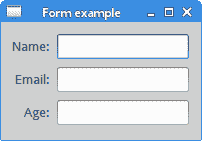
图:简单 form
QGridLayout
QGridLayout将其小部件放置在网格中。 它是一个功能强大的布局管理器。
calculator.h
#pragma once
#include <QWidget>
class Calculator : public QWidget {
public:
Calculator(QWidget *parent = 0);
};
头文件。
calculator.cpp
#include <QGridLayout>
#include <QPushButton>
#include "calculator.h"
Calculator::Calculator(QWidget *parent)
: QWidget(parent) {
QGridLayout *grid = new QGridLayout(this);
grid->setSpacing(2);
QList<QString> values({ "7", "8", "9", "/",
"4", "5", "6", "*",
"1", "2", "3", "-",
"0", ".", "=", "+"
});
int pos = 0;
for (int i=0; i<4; i++) {
for (int j=0; j<4; j++) {
QPushButton *btn = new QPushButton(values[pos], this);
btn->setFixedSize(40, 40);
grid->addWidget(btn, i, j);
pos++;
}
}
setLayout(grid);
}
我们创建计算器的骨架。
QGridLayout *grid = new QGridLayout(this);
grid->setSpacing(2);
我们创建网格布局,并在子小部件之间设置 2px 的空间。
QList<QString> values({ "7", "8", "9", "/",
"4", "5", "6", "*",
"1", "2", "3", "-",
"0", ".", "=", "+"
});
这些是按钮上显示的字符。
for (int i=0; i<4; i++) {
for (int j=0; j<4; j++) {
QPushButton *btn = new QPushButton(values[pos], this);
btn->setFixedSize(40, 40);
grid->addWidget(btn, i, j);
pos++;
}
}
我们将十六个小部件放置到网格布局中。 每个按钮将具有固定的大小。
main.cpp
#include <QApplication>
#include "calculator.h"
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
QApplication app(argc, argv);
Calculator window;
window.move(300, 300);
window.setWindowTitle("Calculator");
window.show();
return app.exec();
}
这是主文件。
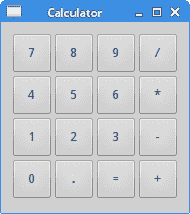
图:QGridLayout
回顾
在本章的下一个示例中,我们使用QGridLayout管理器创建一个更复杂的窗口。
review.h
#pragma once
#include <QWidget>
class Review : public QWidget {
public:
Review(QWidget *parent = 0);
};
头文件。
review.cpp
#include <QGridLayout>
#include <QLabel>
#include <QLineEdit>
#include <QTextEdit>
#include "review.h"
Review::Review(QWidget *parent)
: QWidget(parent) {
QGridLayout *grid = new QGridLayout(this);
grid->setVerticalSpacing(15);
grid->setHorizontalSpacing(10);
QLabel *title = new QLabel("Title:", this);
grid->addWidget(title, 0, 0, 1, 1);
title->setAlignment(Qt::AlignRight | Qt::AlignVCenter);
QLineEdit *edt1 = new QLineEdit(this);
grid->addWidget(edt1, 0, 1, 1, 1);
QLabel *author = new QLabel("Author:", this);
grid->addWidget(author, 1, 0, 1, 1);
author->setAlignment(Qt::AlignRight | Qt::AlignVCenter);
QLineEdit *edt2 = new QLineEdit(this);
grid->addWidget(edt2, 1, 1, 1, 1);
QLabel *review = new QLabel("Review:", this);
grid->addWidget(review, 2, 0, 1, 1);
review->setAlignment(Qt::AlignRight | Qt::AlignTop);
QTextEdit *te = new QTextEdit(this);
grid->addWidget(te, 2, 1, 3, 1);
setLayout(grid);
}
该代码创建了一个窗口,可用于输入作者,书名和书评。
QGridLayout *grid = new QGridLayout(this);
QGridLayout管理器已创建。
grid->setVerticalSpacing(15);
grid->setHorizontalSpacing(10);
我们使用setVerticalSpacing()方法添加垂直间距,并使用setHorizontalSpacing()方法添加水平间距。
QLabel *title = new QLabel("Title", this);
grid->addWidget(title, 0, 0, 1, 1);
这些代码行创建一个标签小部件,并将其放入网格布局中。 addWidget()方法具有五个参数。 第一个参数是子窗口小部件,在本例中为标签。 接下来的两个参数是放置标签的网格中的行和列。 最后,最后一个参数是rowspan和colspan。 这些参数指定当前窗口小部件将跨越多少行。 在我们的情况下,标签将仅跨越一列和一行。
title->setAlignment(Qt::AlignRight | Qt::AlignVCenter);
setAlignment()方法将标题标签对准其单元格。 在水平方向上,它是右对齐的。 在垂直方向上,它居中。
QTextEdit *te = new QTextEdit(this);
grid->addWidget(te, 2, 1, 3, 1);
QTextEdit小部件位于第三行和第二列; 它跨越三行一列。
main.cpp
#include <QApplication>
#include "review.h"
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
QApplication app(argc, argv);
Review window;
window.setWindowTitle("Review");
window.show();
return app.exec();
}
主文件。
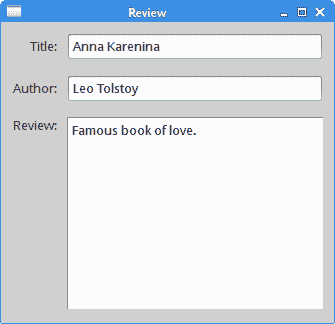
图:回顾
Qt5 教程的这一部分专门用于布局管理。

